A Brief Introduction to 3D Printing
Jonathan Byrne
Natural Computing Research and Applications Group
University College Dublin
Ireland
How do you print three dimensional objects?
- Print a two dimensional object
- Repeat step 1
Stereolithography file (STL)
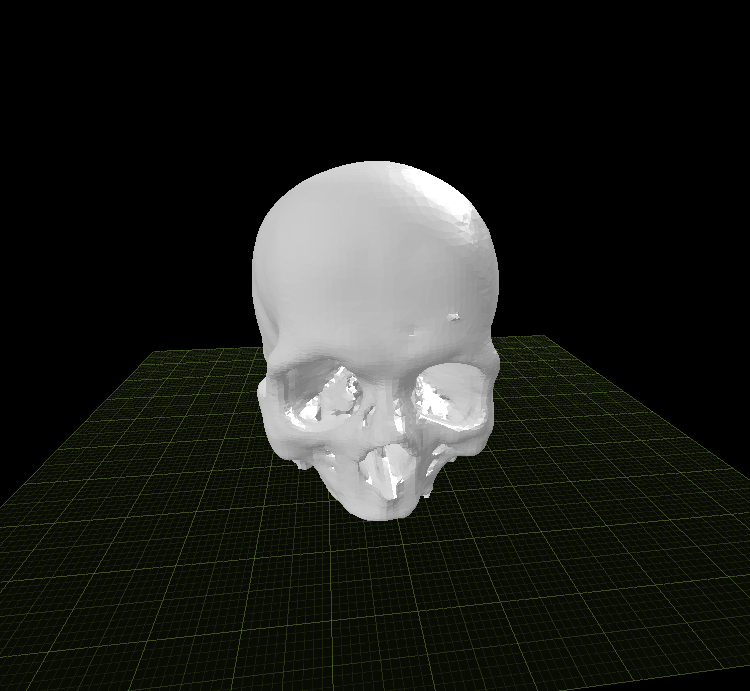
G-code
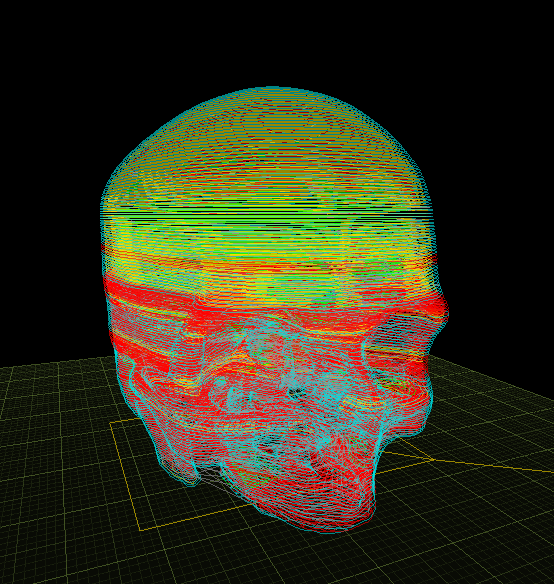
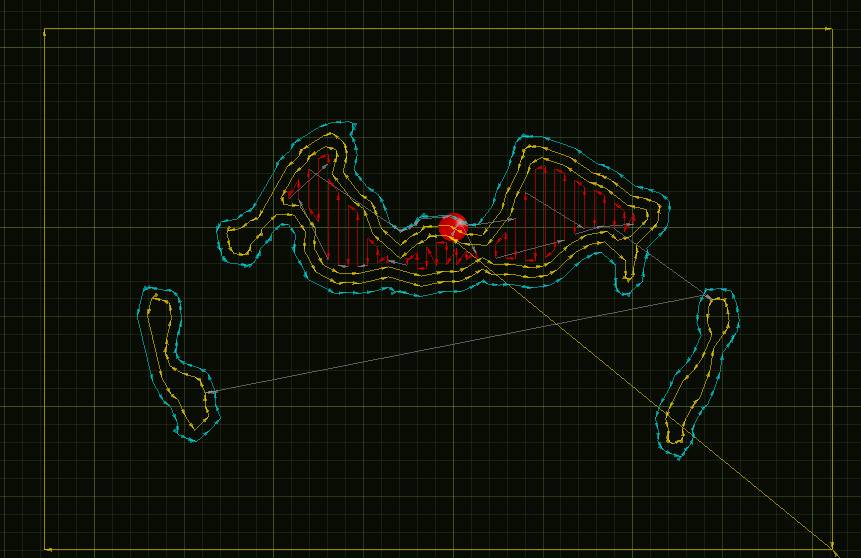
link
How do you actually print it?
- Stereolithography (photo polymer)
- Selective Laser Sintering (powder bed and lasers)
- Plaster-based 3D printing (powder bed and inkjet)
- Laminated object manufacturing (paper, foil, plastic film )
- Fused Deposition Modelling (extrusion)
Fused Deposition Modelling
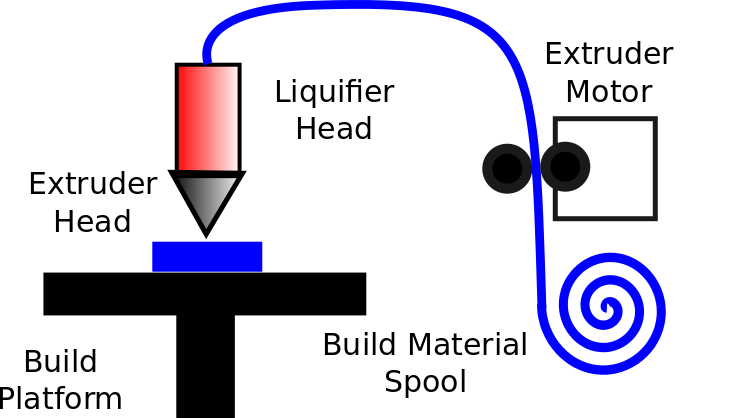
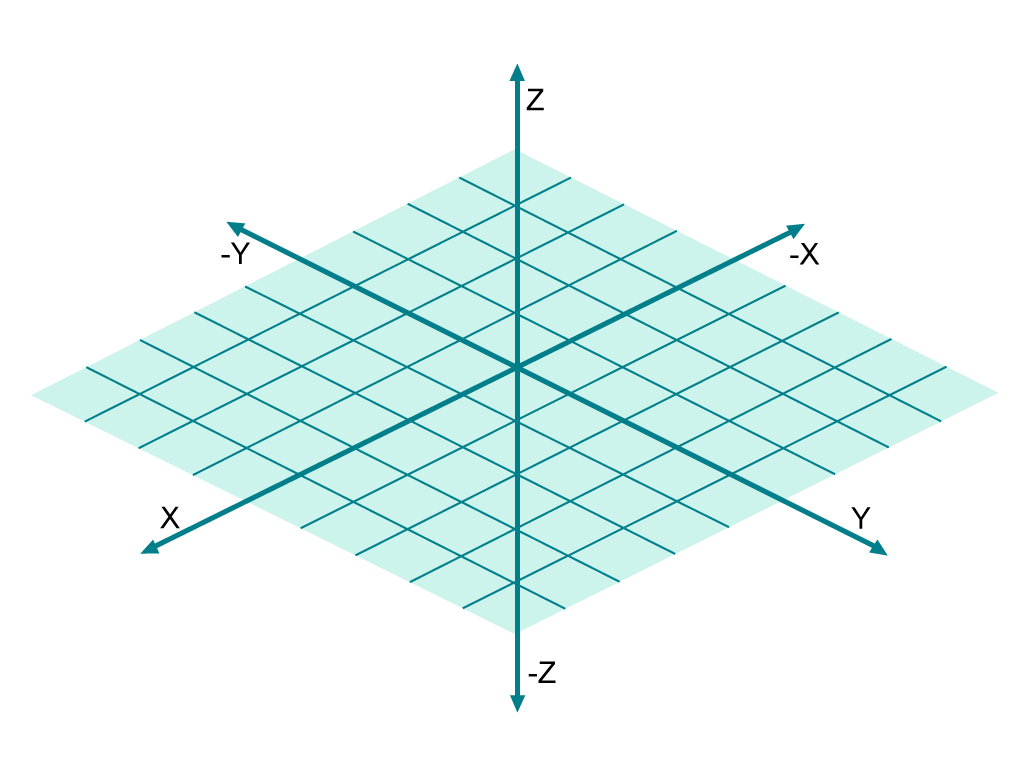
The Axes
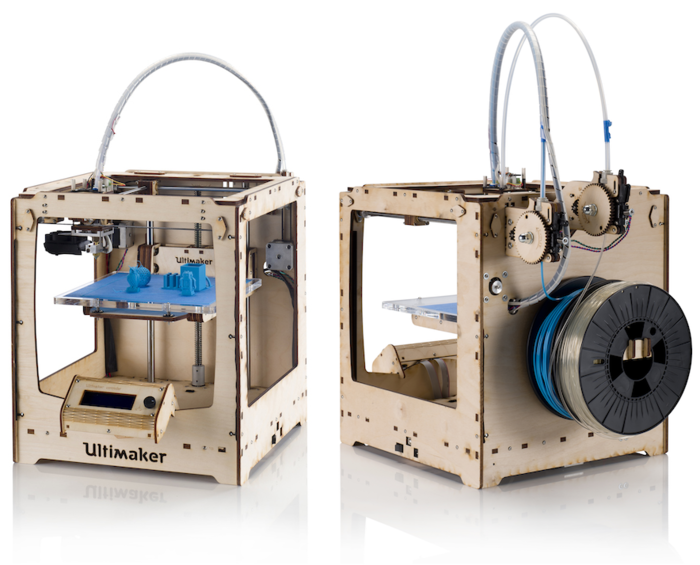
FDM Printer Components
- Frame
- 4 Motors
- 3 endstops (switches)
- Extruder Head
- Electronics
The Ultimaker
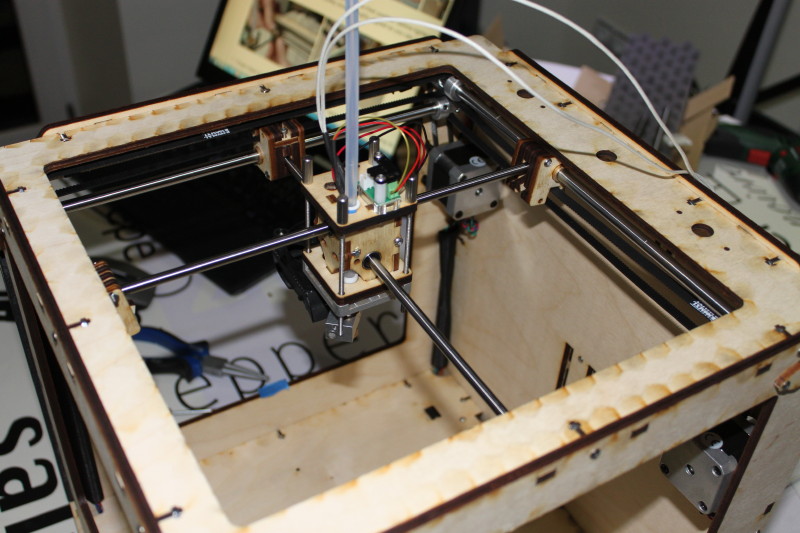
X-Y Axis and Extruder
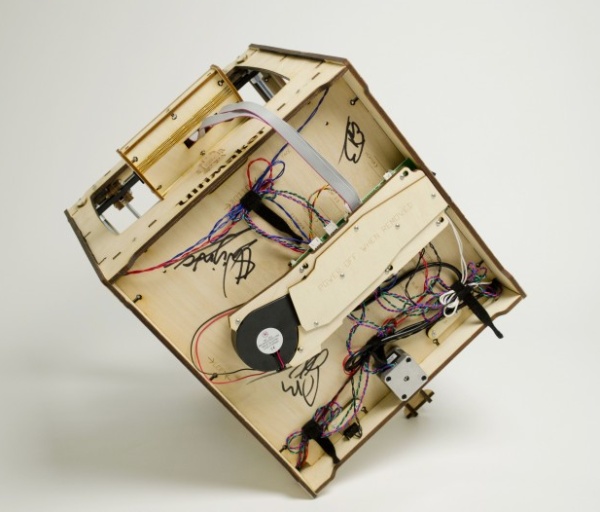
Electronics
What you will need:
- Hex Keys / Allen Keys (1.5mm, 2.0mm)
- Adjustable Wrench
- Pliers
- Cordless Screw Driver
- WD 40
- Masking Tape
- Sand Paper / File
Advice
- Be patient and RTFM
- Read the comments in the instructions
- Look at the built model
- When in doubt, talk to the other team
- Keep the components separate
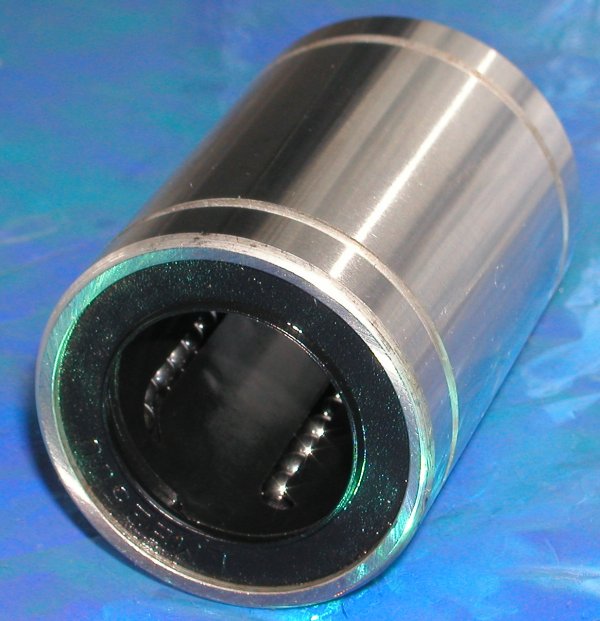
- Take extra care with the linear bearings
- If the regular bearings dont fit, freeze them
Linear Bearing

Regular Bearing

Build Instructions
- Frame: 60-90 minutes
- X-Y Axes: 50-80 minutes (hard!)
- Z Stage: 60-90 minutes
- Extrusion Head: 60-90 minutes (fiddly)
- Material Feed Mechanism: 30-40 minutes
- Electonics: 30-60 minutes
Some final notes
- The ultimaker uses ABS (LEGO plastic) or PLA, use PLA
- Downloadable examples at thingiverse (www.thingiverse.com)
- Every model can be converted to STL
- It may be an STL but it may not be printable
Intersections
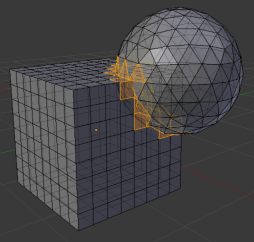
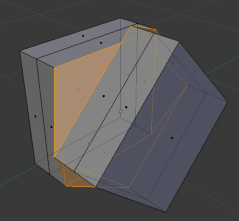
Thin Walls
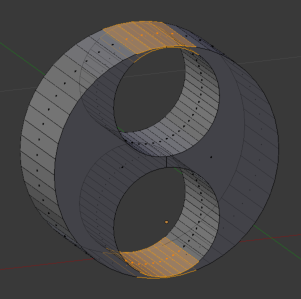
Twisted Planes
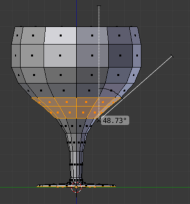
Overhangs
Questions?
- Build instructions: wiki.ultimaker.com/Mechanics_build_guide
- Presentation: www.jonathan-byrne.com/3dprintingintro