A Brief Introduction to 3D Printing
Jonathan Byrne
Urban Modelling Group
University College Dublin
Ireland
How do you print three dimensional objects?
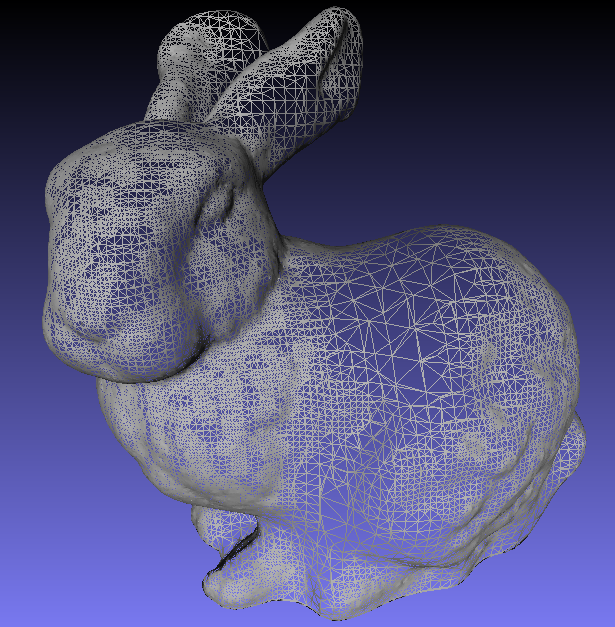
- Create a mesh
- Slice it into layers
- Successively print each layer
Stereolithography file (STL)
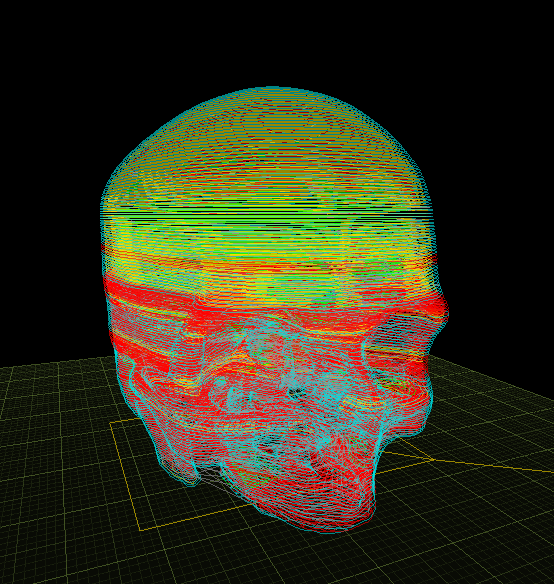
Slicing
G-code
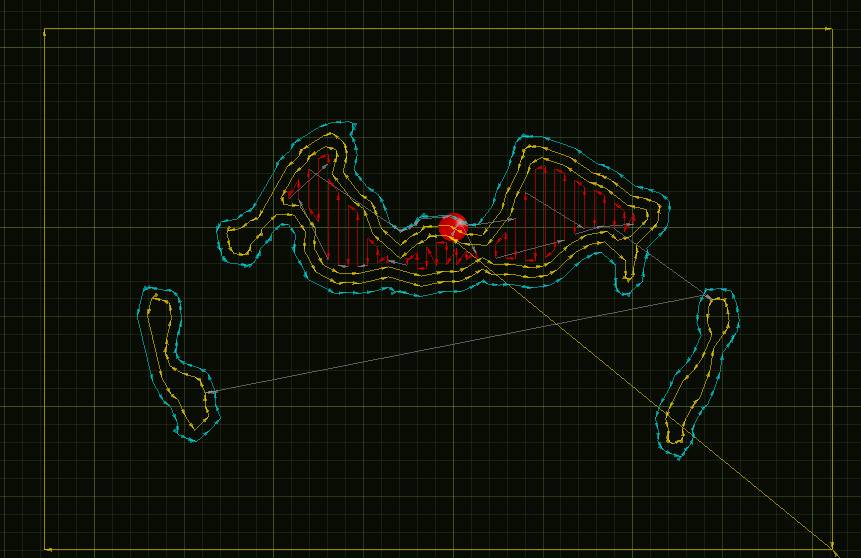
link
3D Printing Technologies
- Stereolithography (photo-curable resin)
- Selective Laser Sintering (powder bed and lasers)
- Plaster-based 3D printing (powder bed and inkjet)
- Fused Deposition Modelling (extrusion)
- Polyjet (photopolymer)
- Laminated object manufacturing (paper, foil, plastic film)
Stereolithography
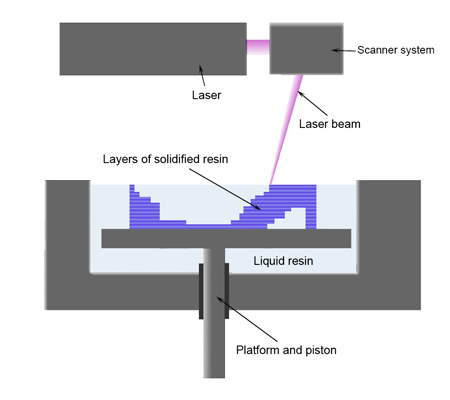
link

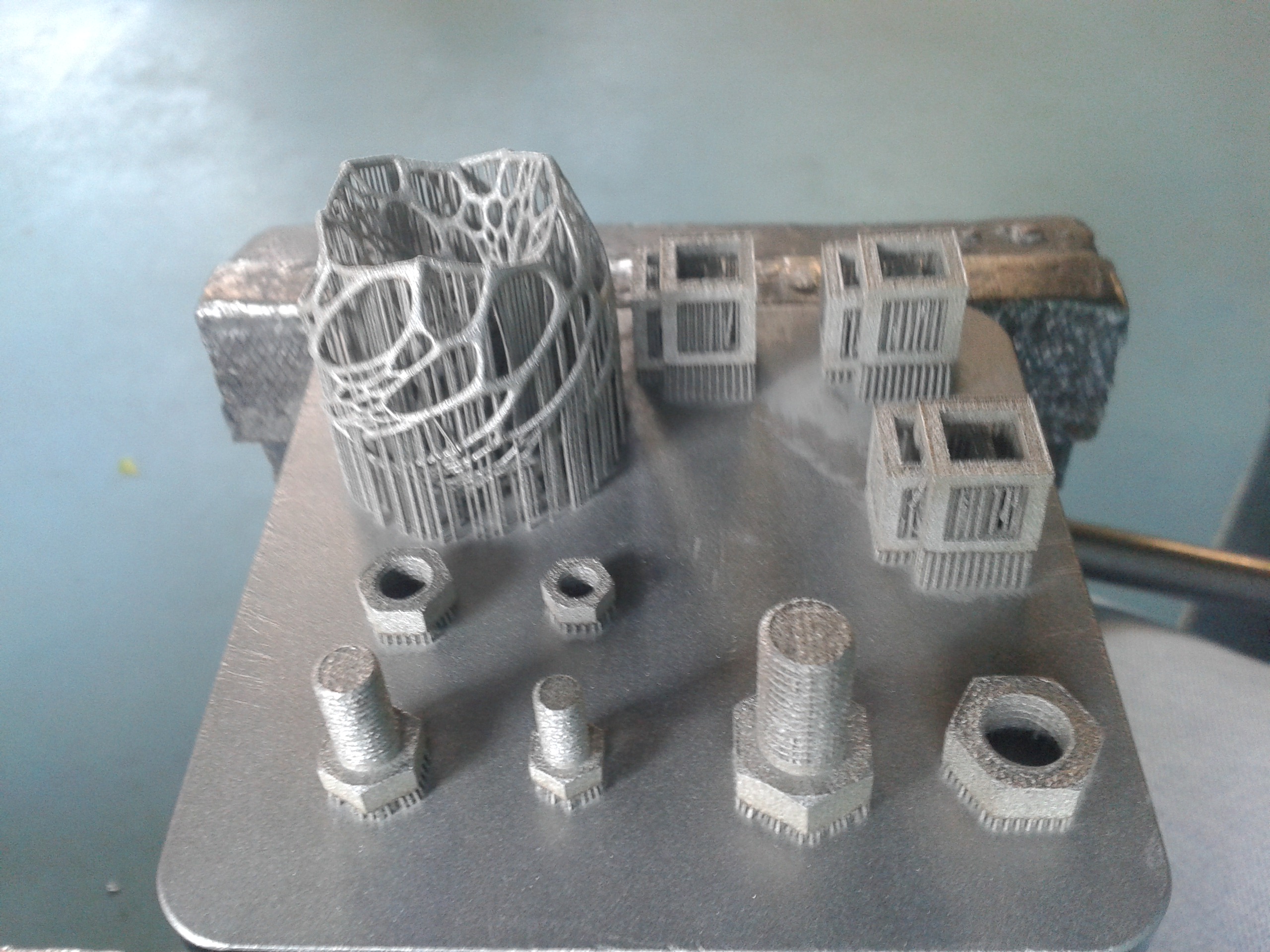
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
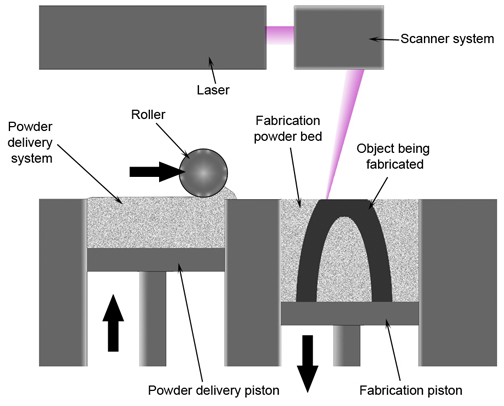
link
Plaster-based 3D Printing (3DP)
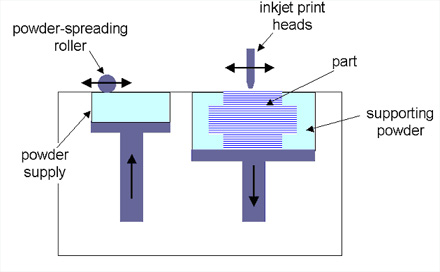
ZCorp
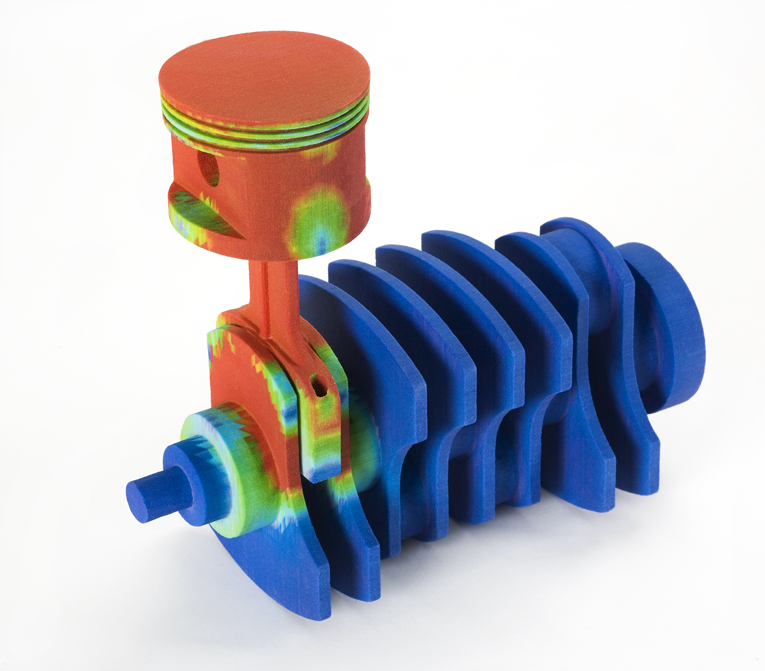

Fused Deposition Modelling
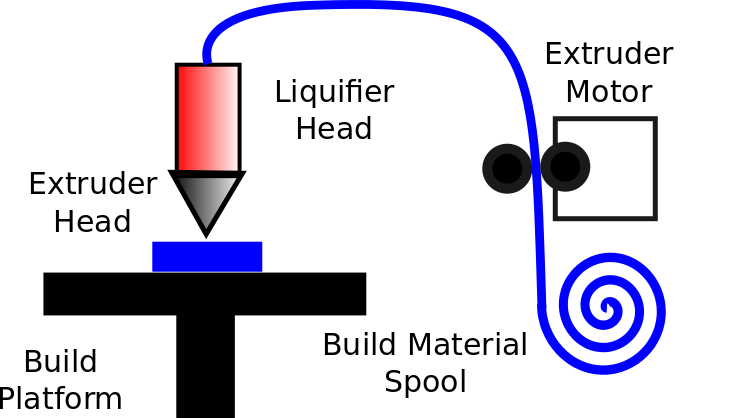
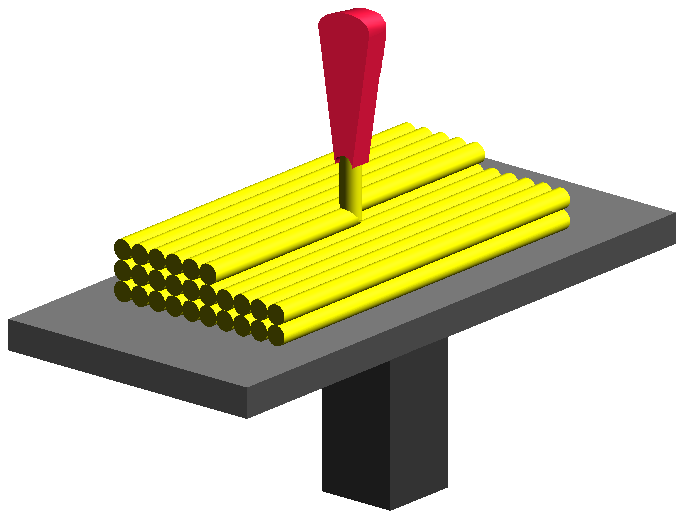
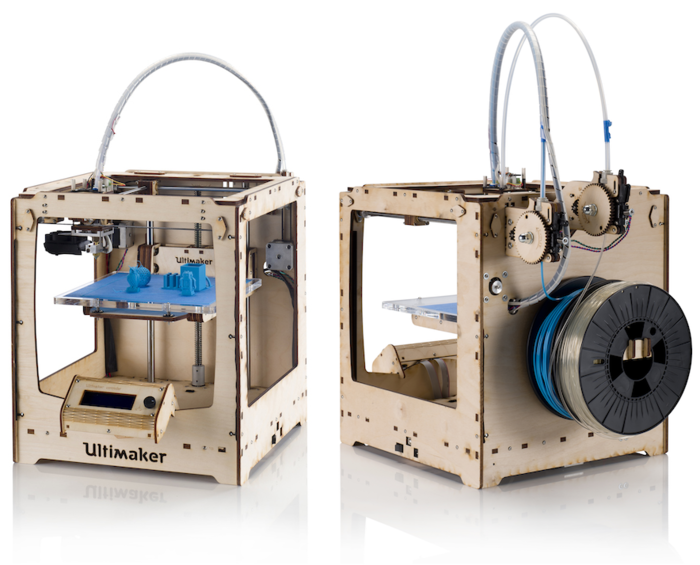
The Ultimaker
link
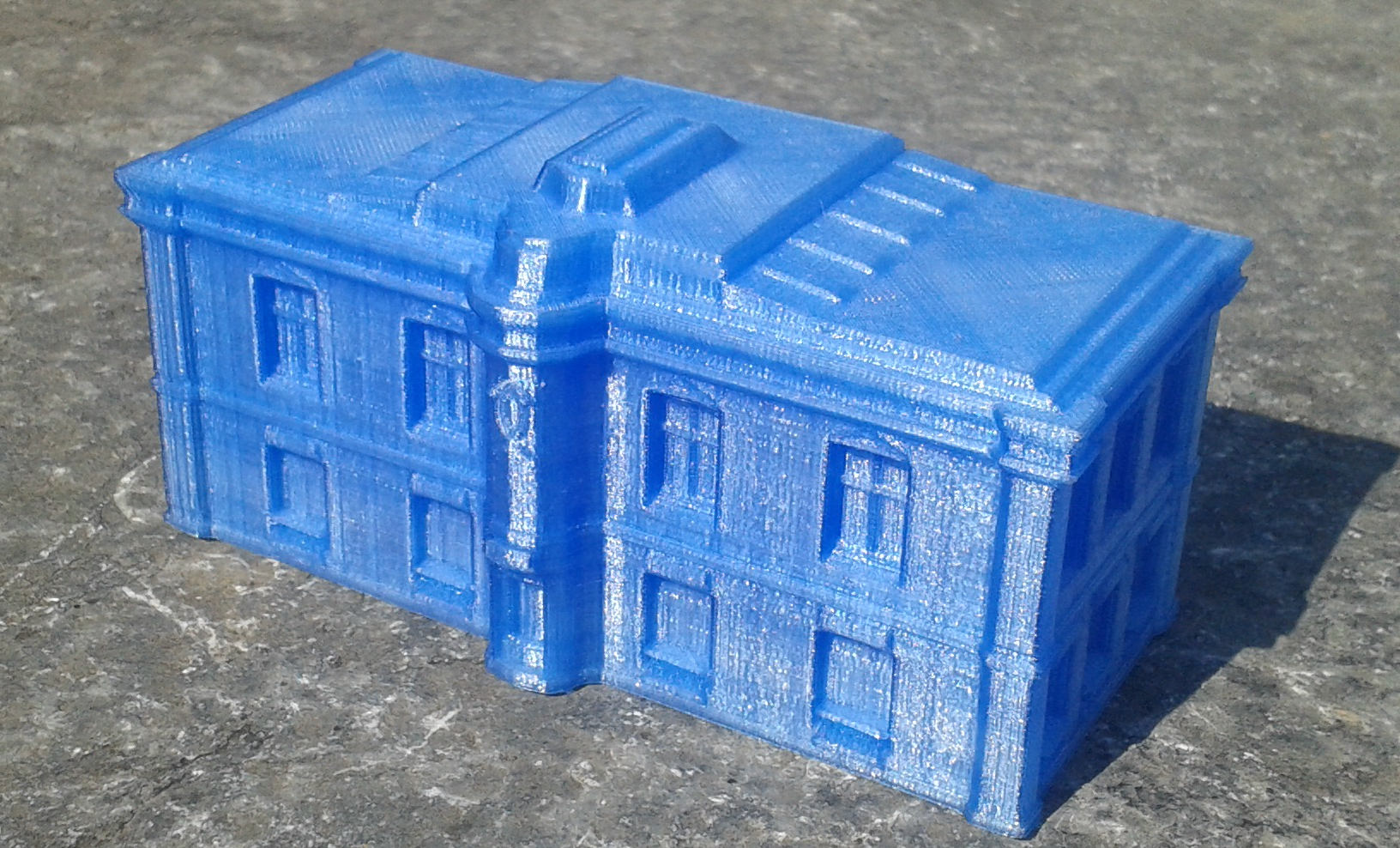

How old is 3D printing?
- 1984: Stereolithography (3D Systems)
- 1985: Selective Laser Sintering (DTM)
- 1990: Fused Deposition Modelling (Stratasys)
- 1993: Powder Bed 3D printing (ZCorp)
- 1998: Photopolymer (Ojet)
RepRap Project

RepRap Project
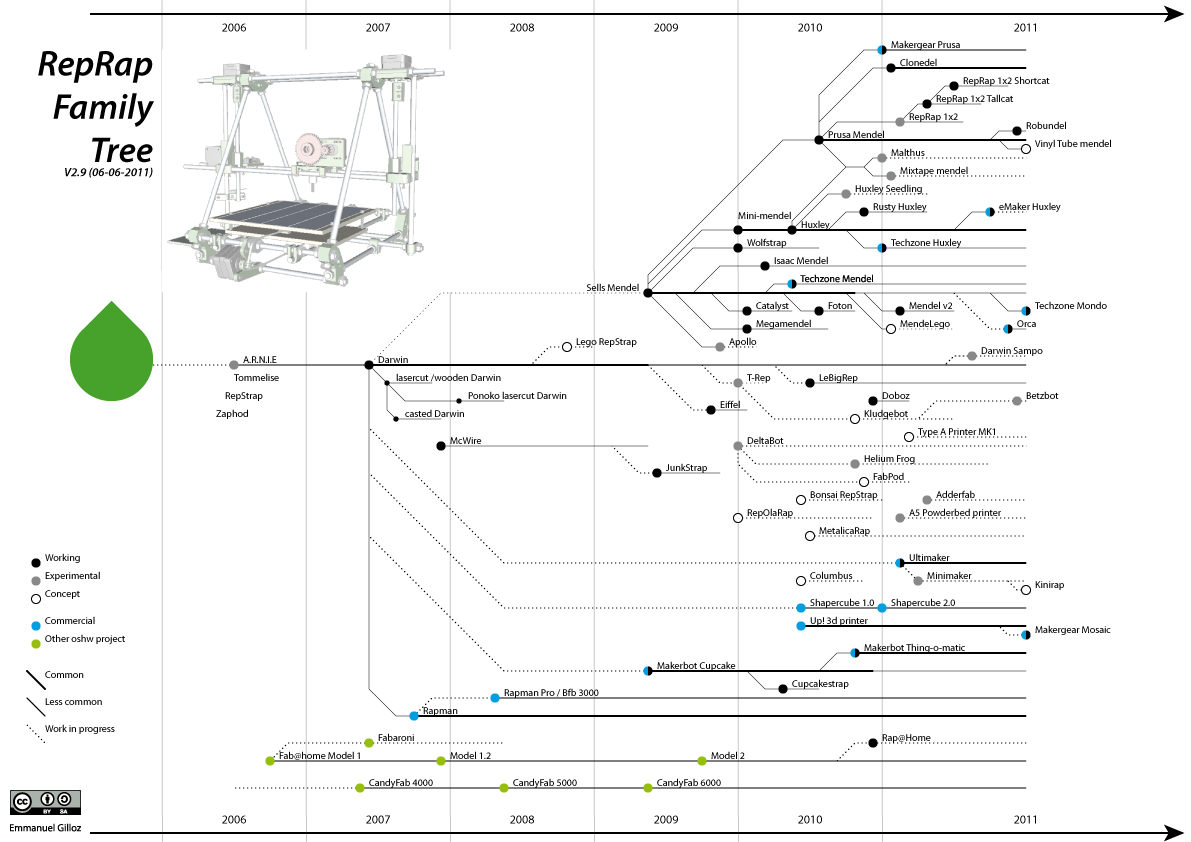
Evolution



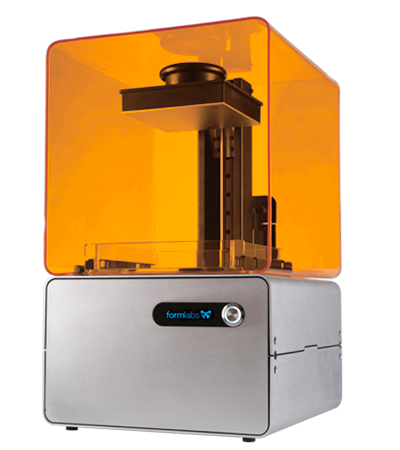
Formlabs Form 1

Design Issues
- Physical limitations
- Gravity
Overhangs
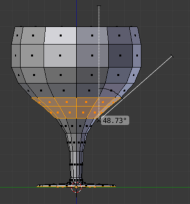
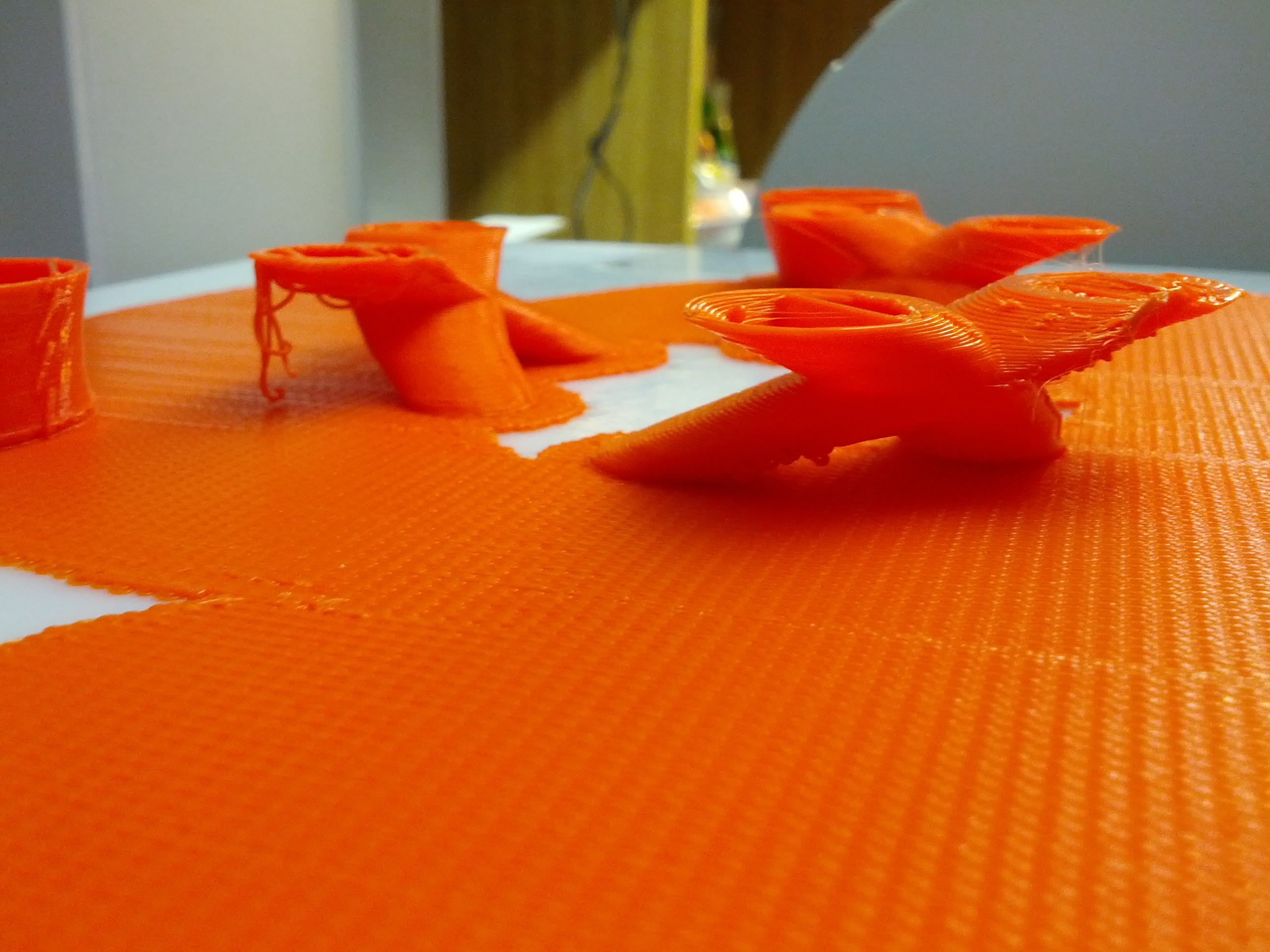

Thin Walls
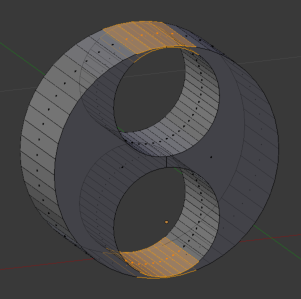
Internal Voids
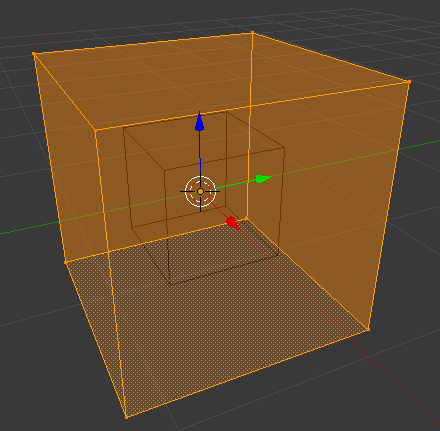
Scale
CAD Issues
- Modelling Software
- Exporting an STL file
- Automated model repair
Water Tightness
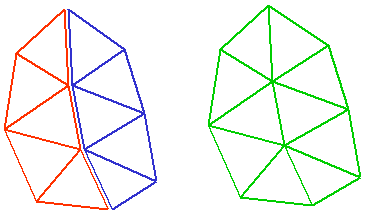
No Thickness
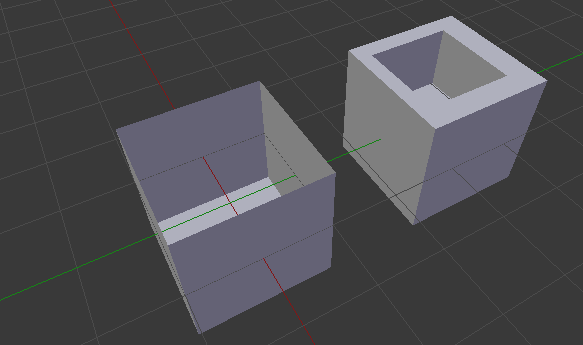
Intersections
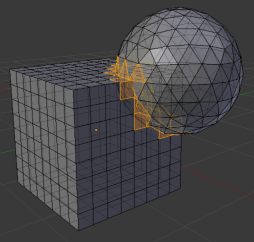
Normals
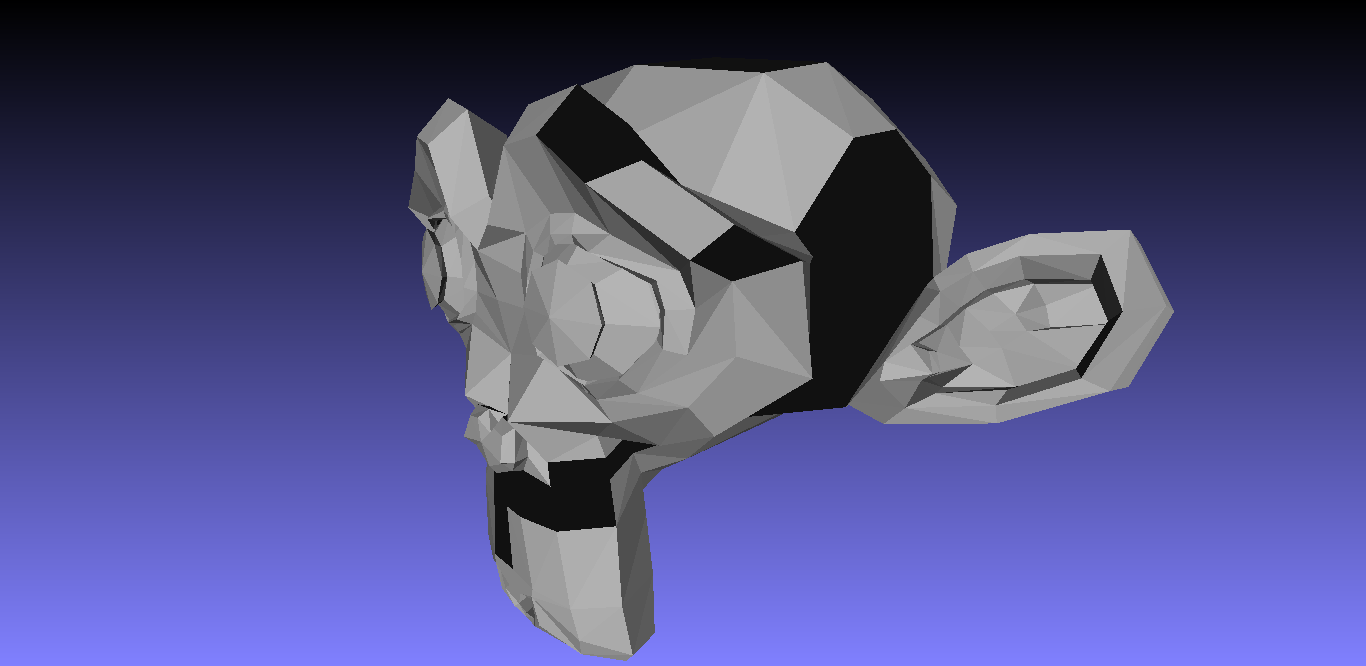
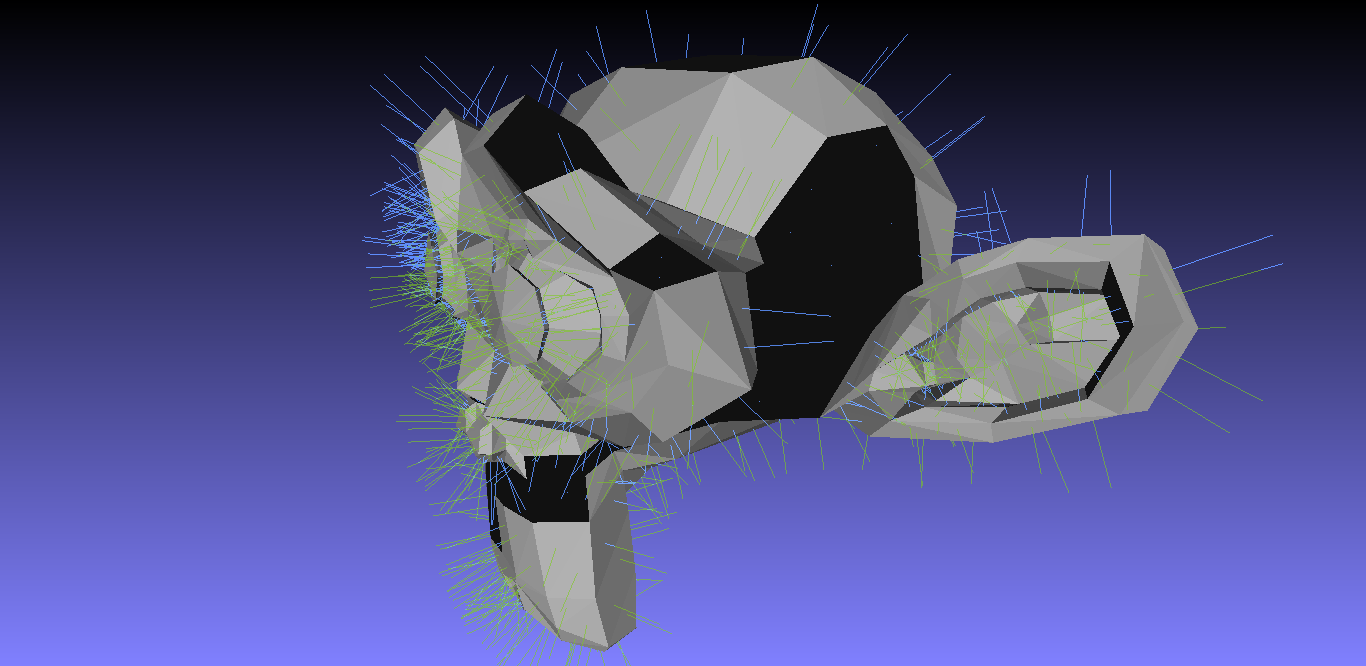
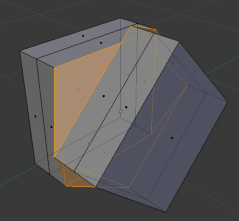
Intersections

Twisted Planes